The Differences Between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Autonomous AI Agents
Which one to choose?
08 January 2025 , Explore the World of CloudOffix
As technology advances, businesses gain access to a wide array of tools designed to optimize operations and enhance efficiency. Among these, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Autonomous AI Agents are frequently mistaken for being synonymous, primarily because both aim to automate tasks and improve efficiency. However, their underlying principles and capabilities differ significantly, leading to distinct applications in business processes.
In reality, these tools fulfill different roles and are built on fundamentally distinct foundations.
What is RPA Robotic Process Automation ?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology designed to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. Think of it as a highly specialized robot trained to execute predefined instructions without deviation. Its structured approach makes it ideal for automating processes such as:
Invoice Processing
Customer Onboarding
Data Entry
While RPA is effective in reducing manual effort, it comes with certain limitations. For example, consider a company using RPA for invoice processing. If the format of incoming invoices changes or additional data fields are introduced, the RPA system will fail to process the new format correctly until reprogrammed. This highlights the static nature of RPA and its dependency on predefined rules, making it less adaptable to dynamic environments.
Static Rules: RPA follows strict workflows and cannot adapt to changes unless reconfigured.
No Decision-Making: RPA lacks the ability to think or respond dynamically, limiting its functionality to executing tasks exactly as programmed.
High Maintenance: Any changes to workflows or processes require frequent updates and human intervention, making it resource-intensive to maintain.
Despite these constraints, RPA remains a valuable tool for businesses seeking to automate structured, predictable tasks.
What is an Autonomous AI Agent?
An Autonomous AI Agent is an advanced system that uses artificial intelligence to perform tasks independently, making decisions and adapting to new information without requiring constant human intervention. Unlike rule-based systems like RPA, Autonomous AI Agents leverage machine learning, natural language processing, and cognitive capabilities to handle complex, dynamic tasks.
Before diving into the capabilities of Autonomous AI Agents, it's important to recognize their unique strengths in handling dynamic and complex environments. Key features of Autonomous AI Agents include:
Dynamic Decision-Making: Autonomous AI Agents analyze data in real-time, enabling them to make informed decisions and adapt to changing circumstances.
Learning and Improvement: Through machine learning, Autonomous AI Agents continuously improve their performance based on new data and experiences.
Contextual Understanding: With natural language processing and cognitive capabilities, these agents can understand context, interact conversationally, and provide meaningful responses.
Proactive Action: Autonomous AI Agents don't just react; they can anticipate needs, identify opportunities, and take proactive steps to achieve goals.
Examples of tasks Autonomous AI Agents excel at include:
Providing personalized customer support
Automating complex workflows across departments
Analyzing large datasets to generate insights
Acting as virtual assistants for scheduling, recommendations, and decision-making
Autonomous AI agents represent a significant leap forward in automation, capable of addressing tasks that require flexibility, intelligence, and minimal human oversight.
Differences Between RPA and Autonomous AI Agents
While Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has long been the go-to tool for streamlining repetitive tasks, the emergence of Autonomous AI Agentsis redefining what automation can achieve. RPA is best suited for repetitive, rule-based tasks, while Autonomous AI Agents are ideal for complex, adaptive environments requiring intelligent decision-making.
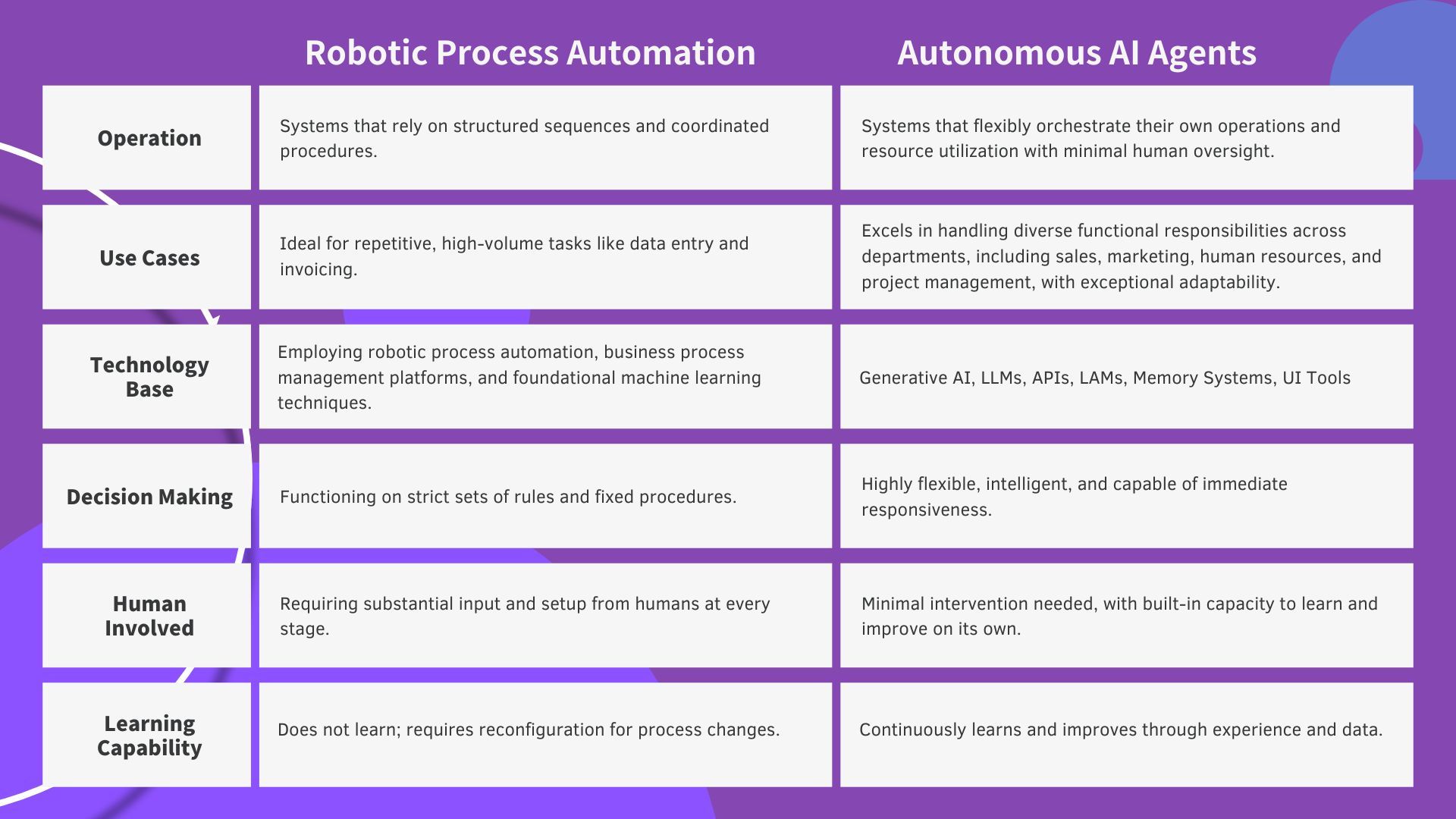
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
The decision between RPA and Autonomous AI Agents depends on the complexity and adaptability required by your business processes:
When to Choose RPA: If your tasks are repetitive, rule-based, and do not require dynamic decision-making, RPA is a cost-effective and efficient choice. It’s particularly useful for automating back-office operations and high-volume processes.
When to Choose Autonomous AI Agents: For tasks that involve decision-making, learning, and adapting to changing scenarios, Autonomous AI Agents are the better option. They are ideal for enhancing customer experiences, optimizing workflows, and handling unpredictable environments.
It’s crucial to recognize the distinct advantages of both Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Autonomous AI Agents, as well as to determine when each one is best suited for your needs. While RPA excels at automating highly structured and rule-based tasks, Autonomous AI Agents provide intelligent, adaptable solutions that can transform your operations.
RPA reliably streamlines processes, executing predetermined tasks such as categorizing tickets or assigning them to the appropriate teams. On the other hand, Autonomous AI Agents operate within the rules and boundaries you set, yet demonstrate cognitive capabilities—enabling them to interpret information, make recommendations, and adapt in real-time.
For example, you could ask an Autonomous AI Agent to:
Classify customer complaints based on a rating scale and category.
Craft an appropriate response for each complaint.
Assign tasks to the relevant customer representatives.
Notify team members about the current status or suggest further actions.
By contrast, RPA alone would simply follow predefined instructions, focusing on tasks like classifying or routing tickets without the capacity to adapt or provide tailored suggestions.
We hope this explanation sheds light on the difference between RPA and Autonomous AI Agents. For more information, please visit our Autonomous AI Agents page.
